Convex hull and Alpha Shapes
In this article, I am going to present what is a convex hull, what is its purpose and how can we construct it in Python. Then I enter into more details by defining an Alpha Shape and constructing it using a triangulation method.
Convex Hull
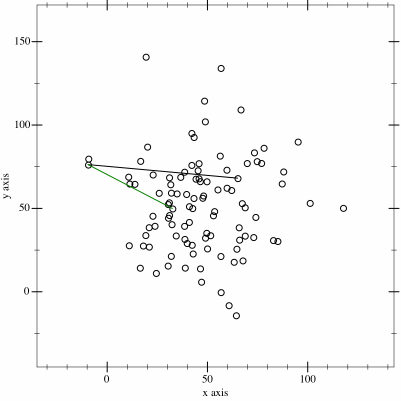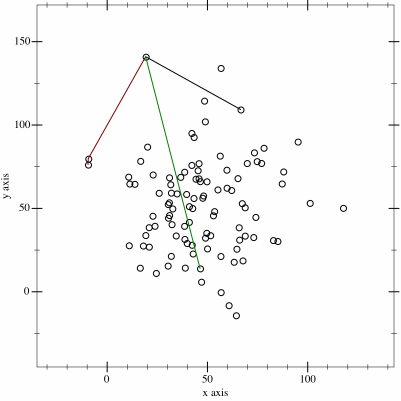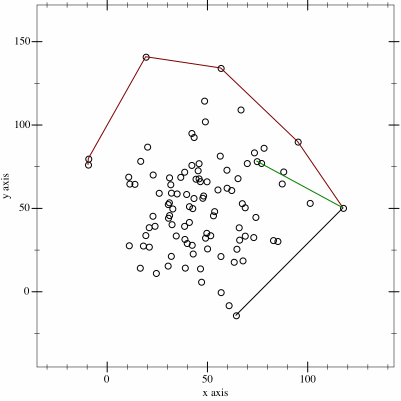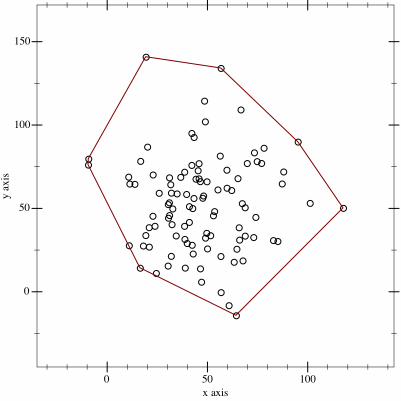
The main idea behind a convex hull comes from the definition of a convex polygon. As a reminder, a convex polygon is a polygon with all its interior angles less than 180°. By using this definition, we figure out that every regular polygon is convex. If one angle has more than 180°, the polygon is considered to be concave. A convex hull uses the same principle as convex polygon applied to set of points. For instance, a convex hull is the smallest convex polygon containing all the points of a set.
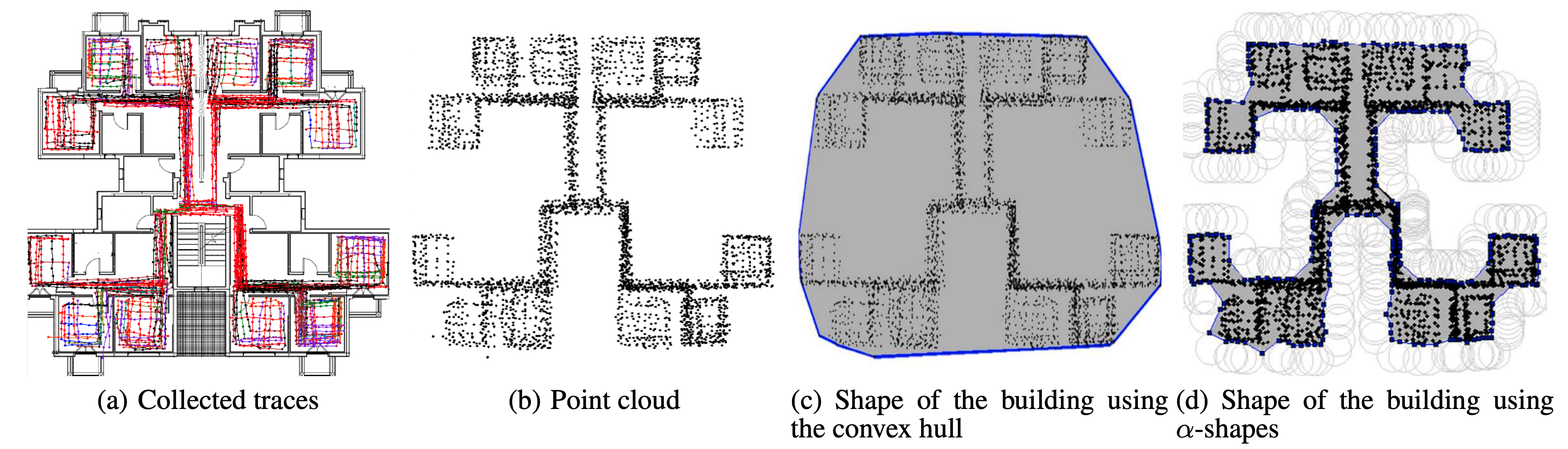
One of the purpose of a convex hull is to prune a specific area in a plane. It is mostly used in computer graphics, geometry and navigation. One interesting use case of convex hull is presented in some papers showing techniques to automatically construct indoor floorplans. One interesting case in presented in this paper written by Alzantot et al. in which they show a method to construct floorplans based on traces collected by ubiquitous sensors. In this paper, they prune a plan and focus only on the area containing the collected traces. By constructing a convex hull on the data points, they present a shape of the indoor floorplan. Another interesting use-case is finding the farthest pair of points in a set in an efficient way. We will dive more into details in the next section when we will present some algorithms used to find convex hulls.
Algorithms:
How to find a convex hull in set of points? Many algorithms are widely used for finding convex hulls, each of them has strenghts and weaknesses as presented below.
Gift Warping Algorithm:
Also known as the Jarvis March, It is one of the most popular and easiest algorithm for finding convex hulls. It works on a simple principle which consists in exploring the n points of a set and returning the list of the points surrounding the set in regard with the properties of a convex hull. This approach requires a O(nm) time complexity in the better case where n is the number of points explored and m is the number of points forming the shape of the hull. In the worst case where n = m, then the time complexity becomes O(n^2). This can easily be huge for a big dataset. To compute a convex hull of a set of points using the Gift Warping Algorithm, we start with the leftmost point p_i (for i = 0) known to be in the convex hull. Then, we select another point p_i+1 such as all the points remaining are on the right of the line drawn between points p_i and p_i+1 and we repeat in loop until we reach the first point p_0.
 .
.
Graham Scan Algorithm:
Alpha Shapes
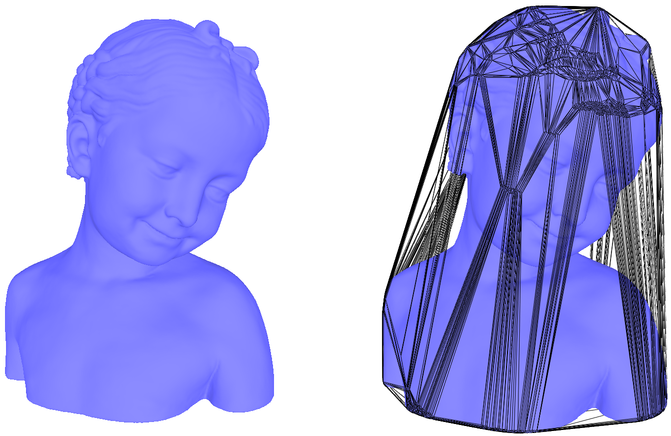
This powerful approach is used to generalize bounding polygons containing a set of points. An interesting use case of Alpha-shapes can be found on this paper. Here, the authors generate floorplans based on collected motion traces. As you can see on the image below, unlike convex hull, alpha shape gives a better precision for finding accurate outline of a set of points. This algorithm is mostly used in computational geometry, especially in processing 3D shapes.
 .
.
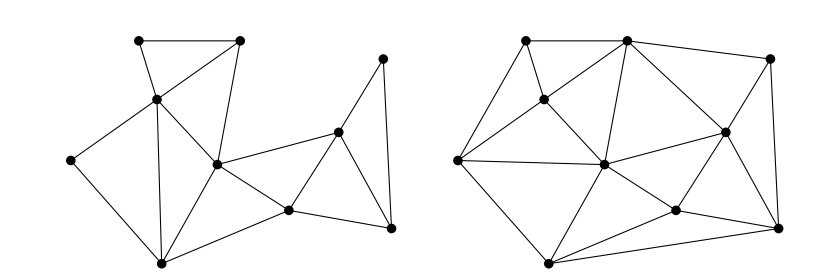
Every Alpha Shape is a convex hull, but not every convex hull is an alpha shape. I will explain why later. First, let us find a way to find the alpha shape of a set of points and let us implement it in Python. The easiest way of finding alpha-shapes is by using… the** Delaunay Triangulation**.
Definition
In mathematics and computational geometry, a Delaunay triangulation (also known as a Delone triangulation) for a given set P of discrete points in a plane is a triangulation DT(P) such that no point in P is inside the circumcircle of any triangle in DT(P). Delaunay triangulations maximize the minimum angle of all the angles of the triangles in the triangulation; they tend to avoid sliver triangles. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delaunay_triangulation
In this context, consider a triangulation as a partition of a polygons into nice triangle. More formally, a triangulation of a finite point set P ⊂ R2 consists in a collection T of triangles, such that:
- conv(P) = ST∈TT;
- P =ST∈T V(T); and
- for every distinct pair T, U ∈ T, the intersection T ∩ U is either a common vertex, or a common edge, or empty.
Every set P ⊆ R2 of n > 3 points has a triangulation, unless all points in P are collinear (meaning that all the points stands on the same line).
 .
.
Computing the delaunay triangulation of a point set consists in linking all the points in a way of creating triangles linking all the points then removing all the triangles for which at least one edge exceeds alpha in length.